リッジ回帰の数式を導出・解説します。流れが詳しくわかるよう、丁寧に式変形するよう心がけております。まずは通常の回帰の数式の導出から始め、リッジ回帰の数式の理解につなげます。
線形回帰
リッジ回帰の数式の解説の前に、線形回帰の概要と数式を解説します。
線形回帰の概要
線形回帰では、データの分布を最も良く近似する線形関数を求める。
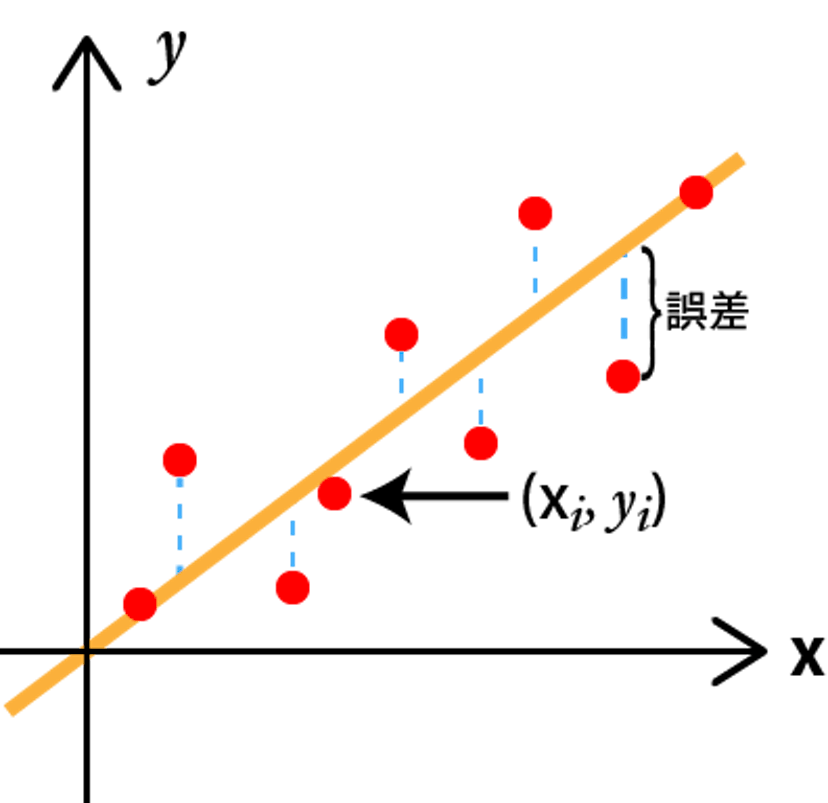
次のようなデータ{(xi,yi)}i=1Nがあるとき、これらのデータを最もよく近似する超平面a⊤x=0を求める。
線形回帰の数式
オレンジの超平面と各データ点の誤差を最小化するような超平面を求めるために、誤差を2乗した損失関数を考え、それを最小化する。2乗誤差を損失関数として利用する理由は、凸なため微分により最小値が求まるためである。
各データ点と超平面の2乗誤差は次のとおりである。
L(a)=i=1∑N(yi−a⊤xi)2=i=1∑N(a⊤xi−yi)2=[x1⊤a−y1⋯xN⊤a−yN]x1⊤a−y1⋮xN⊤a−yN=x1⊤a−y1⋮xN⊤a−yN⊤x1⊤a−y1⋮xN⊤a−yN=x1⊤a−y1⋮xN⊤a−yN2=x1⊤⋮xN⊤a−y1⋮yN2=∥Xa–y∥2
∇aL=0と微分して0とおき、aを求めると、
0X⊤Xa∴a=2X⊤(Xa−y)=X⊤y=(X⊤X)−1X⊤y
このaをa⊤x=0に代入することにより、超平面が求まる。
なお、行列の微分による式変形がわからない方は、以下の記事を参考にされたし。
リッジ回帰
リッジ回帰の概要
線形回帰の2乗誤差を最小化する過程において、複雑さを抑えるために、超平面の重みベクトルaのl2ノルムも同時に最小化する。
すなわち、次の式を最小化する。
i=1∑N(yi−a⊤xi)2+λ∥a∥22
リッジ回帰の数式
∇aL=0と微分して0とおき、aを求める。線形回帰の式と同様に変形すると、
a=(X⊤X+λI)−1X⊤y
このaをa⊤x=0に代入することにより、超平面が求まる。
発展
カーネルリッジ回帰については、次の記事をご覧ください。